同步操作将从 echo/bankInquiryService 强制同步,此操作会覆盖自 Fork 仓库以来所做的任何修改,且无法恢复!!!
确定后同步将在后台操作,完成时将刷新页面,请耐心等待。
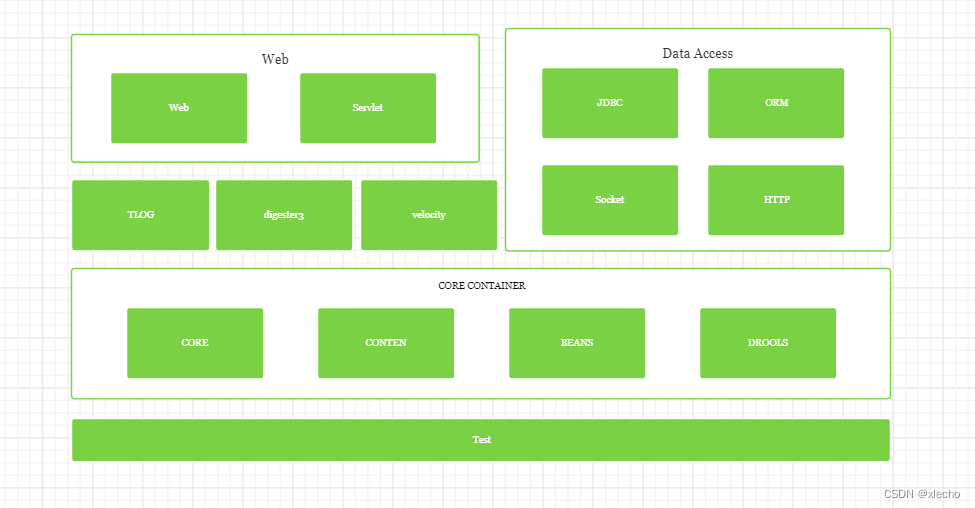
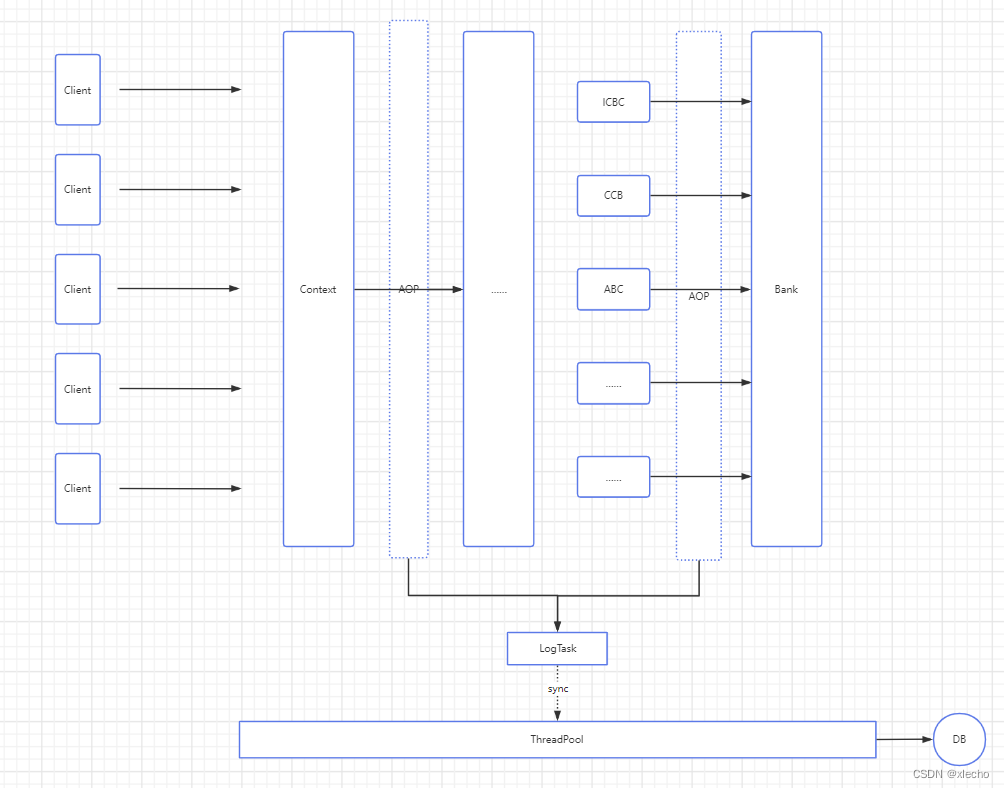
银行查询服务的设计初衷是:为提供更加便利的查询服务,我们在分布式系统架构下,独立开发了与各大银行对接的查询服务。该独立服务支持用户轻松查询账户余额和消费明细的信息,同时保证用户消费的可见性。这种架构设计,不仅提升了用户的查询体验、保证了用户的信息安全,更为整个分布式系统的性能和可维护性提供了保障,为用户和第三方支付机构的长期合作奠定了良好的基础。该服务设计以微服务为基础,使用多种设计模式。如:单例,工厂,模板,策略等。其中对于IOC和AOP的应用是系统逻辑结构设计的最核心部分,在高并发的服务下,为了保证数据的安全性,我们利用IOC和工厂构建的方式,将每个请求流程独立,保证每个请求之间数据独立。AOP的利用为整个系统提供了更好的全局处理方案,并且对对接多家银行因为标准不一的问题提供了统一的解决平台,解决了多家银行之间不能够有效统一返回。 The original intention of designing bank query services is to provide more convenient query services. We have independently developed query services that interface with major banks under a distributed system architecture. This independent service supports users to easily query account balance and consumption details, while ensuring visibility of user consumption. This architecture design not only improves users' query experience and ensures their information security, but also provides guarantees for the performance and maintainability of the entire distributed system, laying a good foundation for long-term cooperation between users and third-party payment institutions. The service design is based on microservices and uses multiple design patterns. For example: single instance, factory, template, strategy, etc. The application of IOC and AOP is the most core part of system logic structure design. In high concurrency services, in order to ensure data security, we use IOC and factory construction methods to make each request process independent and ensure data independence between each request. The utilization of AOP provides a better global processing solution for the entire system, and provides a unified solution platform for connecting multiple banks due to different standards, solving the problem of not being able to effectively unify returns between multiple banks.
| 工具 | 版本 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| IDEA | 2019.2 | |
| JDK | 1.8 | |
| MySQL | 5.7 | 5.7 + |
| 技术 | 描述 | 用途 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SpringBoot | 基础框架 | 构建系统架构 | |
| MyBatis | ORM框架 | 构建数据层 | |
| Maven | 项目管理 | 项目管理 | |
| ExecutorService | 线程池 | 分批执行任务 | |
| drools | 规则引擎 | 简化if else | 这里仅简单实现,用于入参校验 |
| tlog | 日志框架 | 链路追踪 | 保障长流程下,日志能够快捷查询 |
| velocity | 模板引擎 | 将bean转stringXml | 银行交互用xml格式的数据 |
| digester3 | XML解析工具包 | 将stringXml转bean | 银行返回的数据格式为stringXml(通过对应的解析模板,将银行返回的stringXml类型的信息转成Bean) |
| fastjson | JSON解析工具 | 将stringJson转bean bean转stringJson | |
| httpclient | http工具 | 银行通信 |
在较高服务请求下,支付服务为了保障服务的高可用将查询整个链路都进行独立,为支付提供更多的操作内存。同时简化支付服务的维护流程,让支付服务代码结构更加的明了简洁。支付服务内部(第二/三方)基本都需要对接各大银行,有些服务甚至接入的银行超过上千家,对于服务的容错、统一各行标准有着高教的要求,项目内部在不断的接入银行的情况,各种特殊代码,补全查漏层出不穷。导致项目出现横向臃肿,以及可维护度大幅降低。为了支付服务更加的清晰,结构更加有利于维护,查询直接独立。重构查询服务。
public interface ProcessHandler {
ResultContext invoke(QueryContext queryContext);
}
public abstract class AbstractProcessHandler implements ProcessHandler {
@Override
public ResultContext invoke(QueryContext queryContext) {
String queryFlag = queryContext.getQueryFlag();
log.info("开始执行查询,查询类型为:{}", queryFlag);
// 参数校验
checkParam(queryContext);
// 公共参数补齐
paramComplement(queryContext);
// 负载均衡
loadBalance(queryContext);
// 执行查询
if (QueryFlag.BALANCE.getDesc().equals(queryFlag)) {
return this.queryBalance(queryContext);
}
if (QueryFlag.DETAIL.getDesc().equals(queryFlag)) {
return this.queryDetail(queryContext);
}
return new ResultContext();
}
private void loadBalance(QueryContext queryContext) {
SpringboardMachineAddrService springboardMachineAddrService = SpringContextUtils.getBean("springboardMachineAddrService", SpringboardMachineAddrService.class);
List<SpringboardMachineAddr> springboardMachineAddrs = springboardMachineAddrService.selectByBankCode(queryContext.getBankCode());
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(springboardMachineAddrs)) {
throw new BankException("未查询到对应的负载均衡地址信息!");
}
Random rand = new Random();
int randomIndex = rand.nextInt(springboardMachineAddrs.size());
SpringboardMachineAddr springboardMachineAddr = springboardMachineAddrs.get(randomIndex);
queryContext.setChannelId(springboardMachineAddr.getChannelId());
queryContext.setMachineId(springboardMachineAddr.getMachineId());
queryContext.setSignIp(springboardMachineAddr.getSignIp());
queryContext.setSignPort(springboardMachineAddr.getSignPort());
queryContext.setTradeIp(springboardMachineAddr.getTradeIp());
queryContext.setTradePort(springboardMachineAddr.getTradePort());
}
private void paramComplement(QueryContext queryContext) {}
private void checkParam(QueryContext queryContext) {
log.info("开始执行规则引擎参数校验");
KieSession kieSession = SpringContextUtils.getBean("kieSession", KieSession.class);
// 执行某个组的规则
kieSession.getAgenda().getAgendaGroup("checkParam").setFocus();
kieSession.insert(queryContext);
// 执行所有规则
kieSession.fireAllRules();
// 执行指定规则
// kieSession.fireAllRules(new AgendaFilter() {
// @Override
// public boolean accept(Match match) {
// String ruleName = match.getRule().getName();
// return Objects.equals(ruleName, "checkQueryBalanceParamCurrencyCode");
// }
// });
kieSession.dispose();
log.info("规则引擎参数校验完成");
}
protected abstract ResultContext queryBalance(QueryContext queryContext);
protected abstract ResultContext queryDetail(QueryContext queryContext);
}
public class ICBC10201 extends AbstractProcessHandler {
@Override
protected ResultContext queryBalance(QueryContext queryContext) {
log.info("开始执行余额查询!方法:queryBalance被执行");
// bean to string xml
String s = javaBeanToStrXml(queryContext);
log.info("bean to string xml success! xml content: {}", s);
// to bank sign
String signMsg = "urj&*^534faj;";
String signStr = sign(signMsg);
log.info("sign success! signStr: {}", signStr);
// send query content into bank
String result = sendQueryContentIntoBank(signStr + JSON.toJSONString(queryContext));
// string xml to bean
BalanceResult balanceResult = strXmlToJavaBean(bankDataModel(), queryContext);
log.info("string xml to bean sccess! bean content: {}", JSON.toJSONString(balanceResult));
ResultContext resultContext = new ResultContext();
resultContext.setStatus("0000");
resultContext.setBalanceResult(balanceResult);
return resultContext;
}
@Override
protected ResultContext queryDetail(QueryContext queryContext) {
log.info("开始执行明细查询!方法:queryDetail被执行");
ResultContext resultContext = new ResultContext();
resultContext.setStatus("0000");
return new ResultContext();
}
private String sendQueryContentIntoBank(String queryContent) {
SocketConnector socketConnector = new SocketConnector("127.0.0.1", 8081);
return socketConnector.request(queryContent);
}
private String sign(String signMsg) {
return HttpUtils.sendPostJson(signMsg, "");
}
private String javaBeanToStrXml(QueryContext queryContext) {
String ruleModeName = "templates/request-" + queryContext.getBankCode() + "-" + queryContext.getQueryFlag() + ".vm";
ParserEngine parserEngine = SpringContextUtils.getBean("parserEngine", ParserEngine.class);
Map<String, Object> stringObjectMap = JSON.parseObject(JSON.toJSONString(queryContext), new TypeReference<Map<String, Object>>() {
});
return parserEngine.beanToStringXml(ruleModeName, stringObjectMap);
}
private BalanceResult strXmlToJavaBean(String bankResultStrXml, QueryContext queryContext) {
ParserEngine parserEngine = SpringContextUtils.getBean("parserEngine", ParserEngine.class);
return parserEngine.parseXml2Object(bankResultStrXml, "response-" + queryContext.getBankCode() + "-" + queryContext.getQueryFlag());
}
private String bankDataModel() {
return "";
}
}
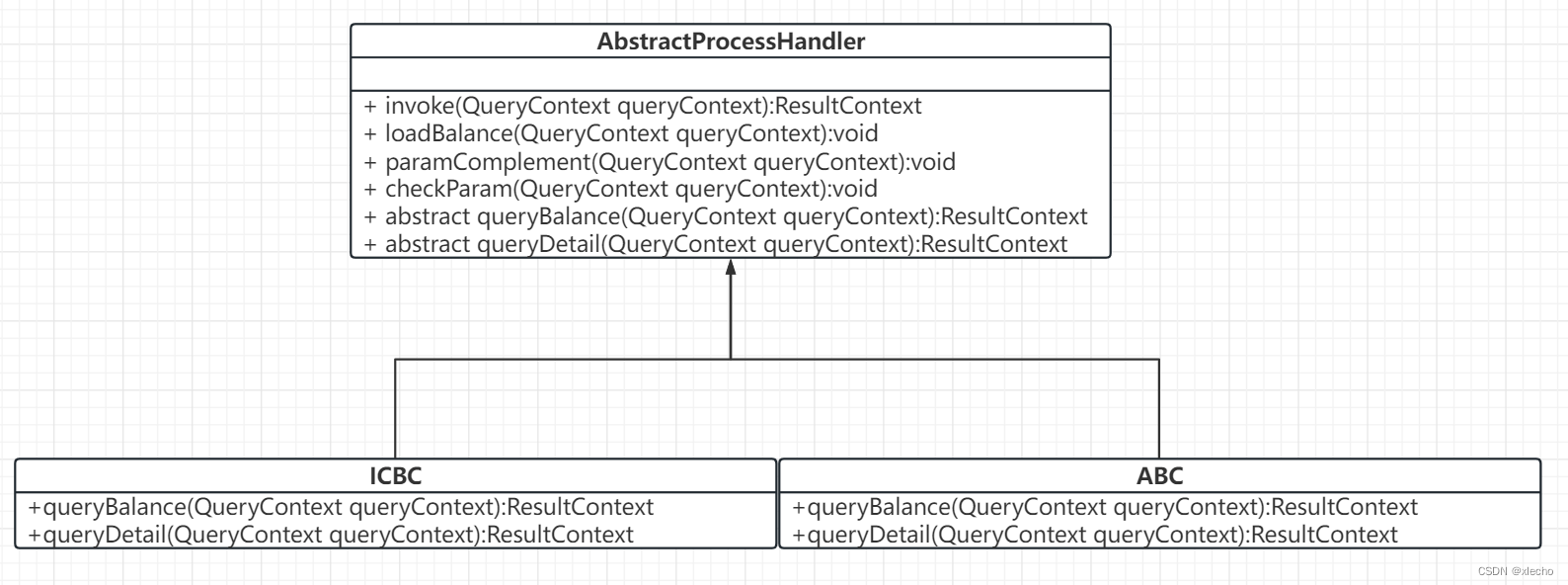
模板方法设计模式是行为型设计模式中的一种,用在一个功能的完成需要经过一系列步骤,这些步骤是固定的,但是中间某些步骤具体行为是待定的,在不同的场景中行为不同。这里定义了具体的整个流程需要执行的步骤,但是对于具体的对接某个银行的方法,还是留给了具体的银行来实现,具体的UML图如下:
if else,这里我们用上策略模式就能完美的解决这些问题,使用了一个接口,就定义了整个查询,让后我们的查询能够在各个银行之间有效的切换。具体实现代码如下:public interface ProcessHandler {
ResultContext invoke(QueryContext queryContext);
}
public abstract class AbstractProcessHandler implements ProcessHandler {
// 此处省略……
}
@Component(value = "102")
public class ICBC10201 extends AbstractProcessHandler {
// 此处省略……
}
// 策略体现
public class BankInquiryController {
public Result<ResultContext> getDetail(@RequestBody QueryContext queryContext) {
ProcessHandler bean = SpringContextUtils.getBean(queryContext.getBankCode(), ProcessHandler.class);
ResultContext invoke = bean.invoke(queryContext);
}
}
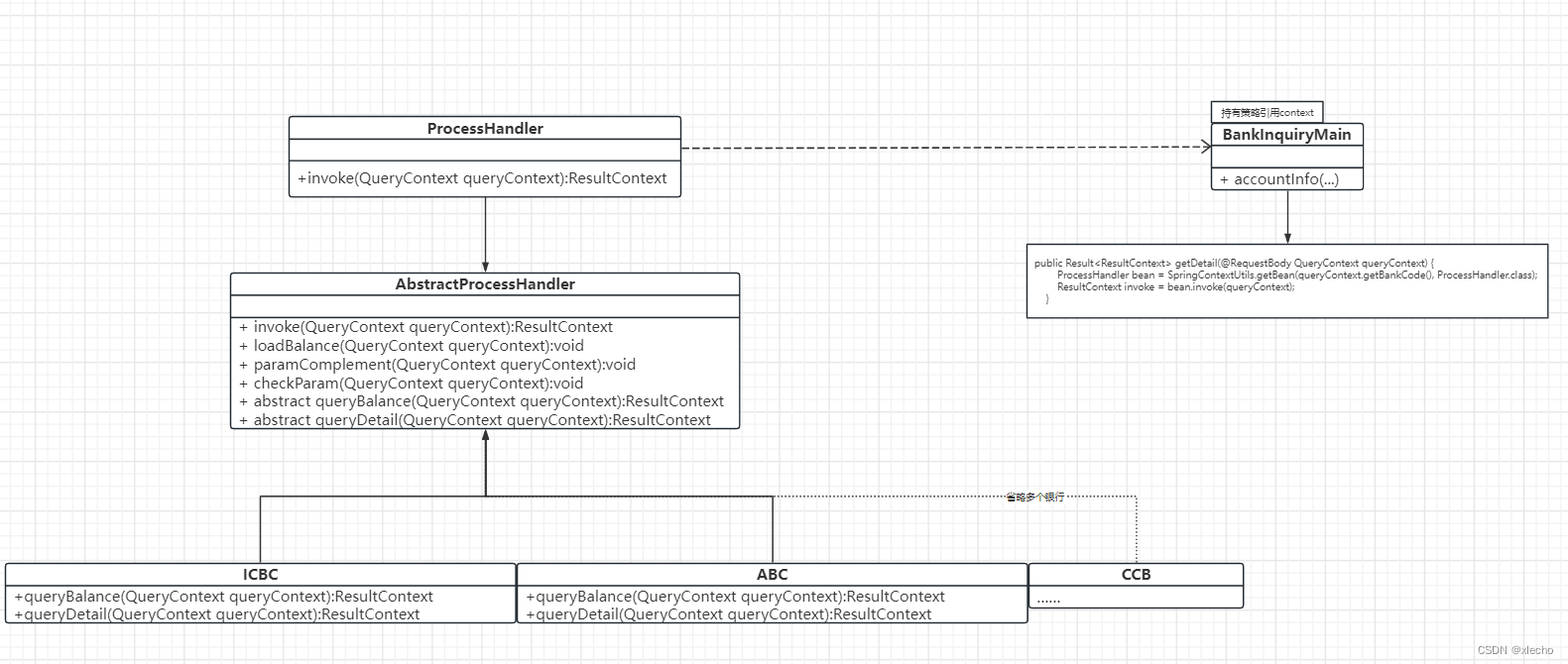
策略模式在这里很有效的去除了if else,同时对外暴露查询功能时,提供了多银行之间自由切换的能力。具体实现UML图如下:
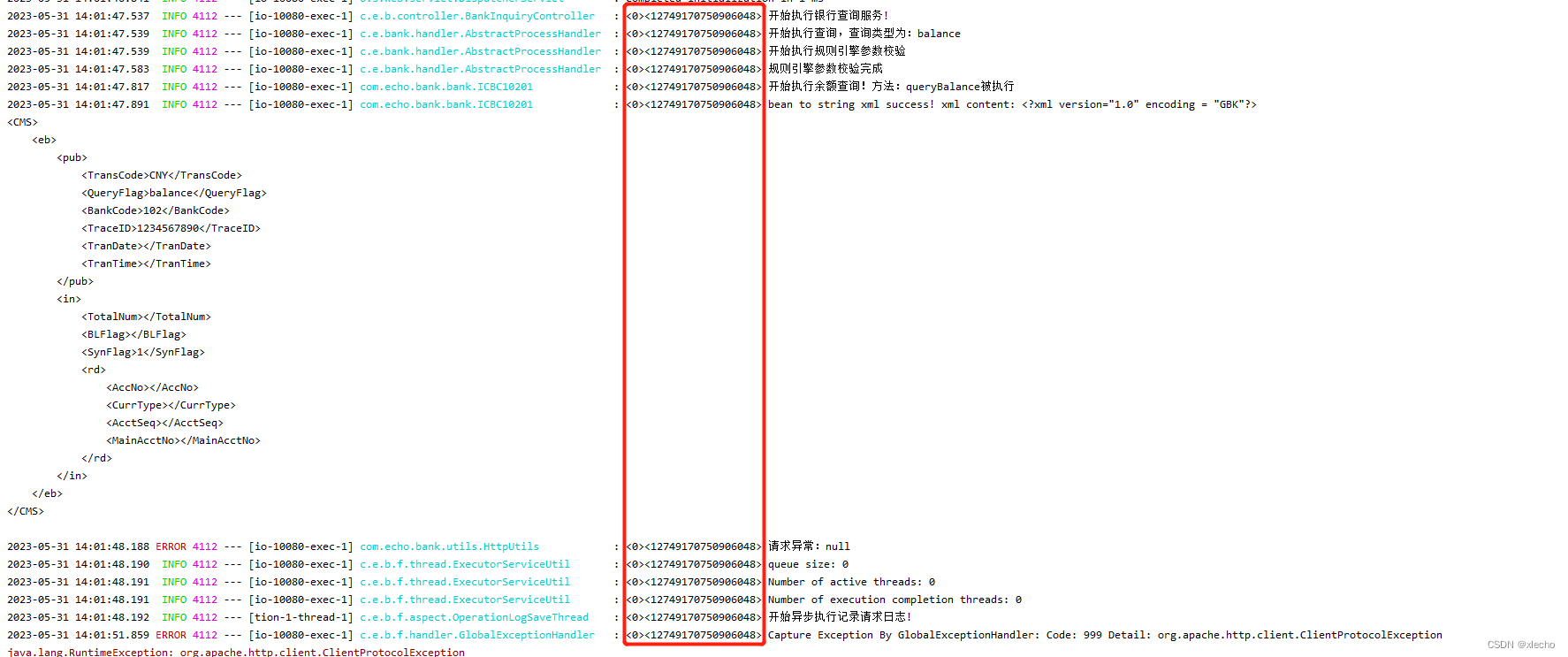
在高并发的情况下,查询如果出现问题,维护也是一个比较复杂的工作,比如:我们需要去排查某一次查询为什么出现了问题的时候,这次出现问题的时间点内请求量很大,那我们需要费一些时间来定位到我们当前日志是不是某一次请求,在整个项目当中每次请求有对应很多日志的情况下,那我们需要把每一行日志对应到这次出问题的请求上,就需要很长的耗时。特别是公司内部,如果都是微服务,把系统拆分的很细的情况下,那上下游的排查就会有很大的定位问题,当然有的小伙伴就会想到使用SkyWalking,Pinpoint等分布式追踪系统来解决,并且这些系统通常都是无侵入性的,同时也会提供相对友好的管理界面来进行链路Span的查询,但是搭建分布式追踪系统还是需要一定的成本的,所以本文要说的并不是这些分布式追踪系统,而是一款简单、易用、几乎零侵入、适合中小型公司使用的日志追踪框架TLog。同时使用TLog也能有效的让我们内部的日志,能够快速的定位到某一次请求的所有日志。TLog会自动的对日志进行打标签,自动生成traceId贯穿你微服务的一整条链路,在排查日志的时候,可以根据traceId来快速定位请求处理的链路。在项目内的表现如下:
对于一个查询来讲其实提到收集日志,可能有人觉得这是多此一举,当我们回顾这个服务的具体功能之后,我们会发现与多家银行的交互,这是对外统一提供服务的,作为一个查询银行的服务,我们需要有效的去保障对接的银行都能够有效的提供服务,这样我们的操作日志就很有必要了。也能有效的去规避一些因为银行而导致的客户投诉。这里的操作日志收集,还是用的老一套,AOP+注解来实现。SpringBoot中做日志的方法有很多,比如用拦截器,在拦截器中进行处理需要进行收集日志的方法,同时也可以将日志存库,但是这种方法可能会有一个弊端,在拦截器中进行处理日志的话,对于请求量过大的系统,或者处理次数过多的,以及并发过高的项目来说,都是一个可怕的性能消耗。aop做日志处理的关键原因,量级小,简单,同时利用线程池异步的方式,有效的环节高并发的请求日志记录问题
定义的注解如下:
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface OperationLog {
/**
* 执行方法功能描述
*/
String desc() default "";
/**
* 1:发送, 0:接收
*/
String type() default "0";
}
在银行查询服务中,数据最关键的不是落库,而是与银行交互,然后处理数据,最终统一返回,所以我们不仅要记录被请求的日志,还需要记录向外发送的请求日志,已报账发送的请求都是符合规范的。这也是为什么需要记录操作日志的主要原因之一
AOP的实现如下:
package com.echo.bank.framework.aspect;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.echo.bank.enums.StatusCode;
import com.echo.bank.framework.ioc.SpringContextUtils;
import com.echo.bank.framework.thread.ExecutorServiceUtil;
import com.echo.bank.pojo.OperateLog;
import com.echo.bank.service.OperateLogService;
import com.echo.bank.utils.RequestUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
/**
* @author echo
* @version 1.0
* Create by 2023/5/25 9:19
*/
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class OperationLogAspect {
@Autowired
private OperateLogService operateLogService;
/**
* 扫描使用这个注解的方法
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.echo.bank.framework.aspect.OperationLog)")
public void logPointCut() {
}
@Around("logPointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
Date beginTime = new Date();
String result = null;
String status = null;
try {
Object obj = point.proceed();
if (obj != null) {
result = JSONObject.toJSONString(obj);
}
status = StatusCode.SUCCESS.getCode() + "";
return obj;
} catch (Exception e) {
//请求执行出错
result = e.getMessage();
status = StatusCode.ERROR.getCode() + "";
throw e;
} finally {
saveLog(point, beginTime, new Date(), result, status);
}
}
/**
* 保存日志
*/
private void saveLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, Date beginTime, Date endTime, String result, String status) {
OperateLog operateLog = new OperateLog();
try {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
OperationLog annotation = method.getAnnotation(OperationLog.class);
if (annotation != null) {
operateLog.setDesc(annotation.desc());
operateLog.setType(annotation.type());
}
if (joinPoint.getArgs() != null) {
try {
operateLog.setParamContext(JSONObject.toJSONString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("解析并记录请求参数出现错误! msg: {}", e.getMessage());
}
}
operateLog.setCreateUser("echo");
operateLog.setCreateTime(beginTime);
operateLog.setUpdateTime(endTime);
operateLog.setStatus(status);
operateLog.setResultContext(result);
setRequestIp(operateLog);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("记录请求日志时初始化日志对象报错! msg: {}", e.getMessage());
}
ExecutorService instance = ExecutorServiceUtil.getInstance();
instance.execute(new OperationLogSaveThread(operateLogService, operateLog));
}
private void setRequestIp(OperateLog operateLog) {
try {
RequestUtils requestUtils = SpringContextUtils.getBean("requestUtils", RequestUtils.class);
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = requestUtils.getHttpServletRequest();
String requestIp = requestUtils.getRequestIp(httpServletRequest);
operateLog.setRequestIp(requestIp);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 向外请求的时候,使用该IP
operateLog.setRequestIp("127.0.0.1");
}
}
}
这里仅仅使用AOP还不能有效的收集日志,这个收集日志的操作还会让我们的系统性能下降,导致查询缓慢。所以我们还需要异步的去执行,这样就能有效的保障日志能被有效的记录,同时不影响系统问题。线程池引入,如下:
@Slf4j
public class OperationLogSaveThread implements Runnable {
private OperateLogService operateLogService;
private OperateLog operateLog;
public OperationLogSaveThread(OperateLogService operateLogService, OperateLog operateLog) {
this.operateLogService = operateLogService;
this.operateLog = operateLog;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("开始异步执行记录请求日志!");
try {
operateLogService.insert(operateLog);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("异步记录日志出现报错!msg: {}", e.getMessage());
}
}
}
public class ExecutorServiceUtil {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExecutorServiceUtil.class);
private static ThreadPoolExecutor executorService;
private static final int INT_CORE_POOL_SIZE = 50;
private static final int MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE = 100;
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 60;
private static final int WORK_QUEUE_SIZE = 2000;
static {
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
INT_CORE_POOL_SIZE,
MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE,
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(WORK_QUEUE_SIZE),
new CommunityThreadFactory(),
new DataMigrationRejectedExecutionHandler());
}
private ExecutorServiceUtil() {
if (executorService != null) {
throw new BankException("Reflection call constructor terminates execution!!!");
}
}
public static ExecutorService getInstance() {
logger.info("queue size: {}", executorService.getQueue().size());
logger.info("Number of active threads: {}", executorService.getActiveCount());
logger.info("Number of execution completion threads: {}", executorService.getCompletedTaskCount());
return executorService;
}
}
public class DataMigrationRejectedExecutionHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
try {
// 核心改造点,由blockingqueue的offer改成put阻塞方法
executor.getQueue().put(r);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class CommunityThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
CommunityThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() : Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "dataMigration-" + poolNumber.getAndIncrement() + "-thread-";
}
/**
* 创建线程
*
* @param r
* @return
*/
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r, namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(), 0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
return t;
}
}
这样的实现,既保障了被调用的时候所有请求的日志都记录了,同时也保障了发送出去的请求也能有效记录。具体图示:
规则引擎的引入主要的原因就两个:1、if else过多,用以简化代码 2、小试牛刀
规则引擎最大的作用就是灵活的将规则和业务剥离,解决了灵活变更规则不影响具体业务的难点。选择Drools的理由:Drools 是用 Java 语言编写的具有一个易于访问企业策略、易于调整以及易于管理的开源业务规则引擎,其基于CHARLES FORGY’S的RETE算法符合业内标准,速度快且效率高
引入的Drools版本如下:
<!--drools规则引擎-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.drools</groupId>
<artifactId>drools-core</artifactId>
<version>7.6.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.drools</groupId>
<artifactId>drools-compiler</artifactId>
<version>7.6.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.drools</groupId>
<artifactId>drools-templates</artifactId>
<version>7.6.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.kie</groupId>
<artifactId>kie-api</artifactId>
<version>7.6.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.kie</groupId>
<artifactId>kie-spring</artifactId>
<version>7.6.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
if(checkParam1) throw new BankExcption("");
if(checkParam2) throw new BankExcption("");
if(checkParam3) throw new BankExcption("");
if(checkParam4) throw new BankExcption("");
if(checkParam5) throw new BankExcption("");
if(checkParam6) throw new BankExcption("");
if(checkParam7) throw new BankExcption("");
这类代码,不仅在我们接口被调用的时候会出现,也会出现在银行返回的时候,对某些特定数据校验,判断当前请求是否成功。如果业务发生变更,或者银行内部变更,我们这边就需要重新编码,然后上线。但是drools的引入就完美的解决了这一问题,我们可以重新编写规则文件,替换规则文件之后,重新加载即可,不需要重新发布系统。同时简化了if else.使用了drools的具体代码如下:
private void checkParam(QueryContext queryContext) {
log.info("开始执行规则引擎参数校验");
KieSession kieSession = SpringContextUtils.getBean("kieSession", KieSession.class);
// 执行某个组的规则
kieSession.getAgenda().getAgendaGroup("checkParam").setFocus();
kieSession.insert(queryContext);
// 执行所有规则
kieSession.fireAllRules();
kieSession.dispose();
log.info("规则引擎参数校验完成");
}
对接银行或者说支付行业的整体技术更新是比较缓慢的,有可能有很多地方还在用ext等老古董框架。在这种前提下, 很多项目的内部往往总是有老框架固定的架构规范,导致内部代码结构难以真正的去修改。这里直接全部打破,使用全新的技术,来重构项目,这样不仅解决了老框架的限制,同时也为我们重构提供了更好的环境。当然新框架带来的问题也会随之而来,比如并发的处理,在老框架中,很多static变量的兼容,虽然拜读了很多,而且也有很完美的处理方案去避免并发,但是如果将这些东西搬到新框架就会带来很多的数据安全问题。所以这里采用了单次请求内数据全部独立的方式。
其核心思想就是每次请求,当前请求的所有数据都不共享。实现的方式也是比较简单的,直接使用了Spring Bean的作用域来解决这类问题。
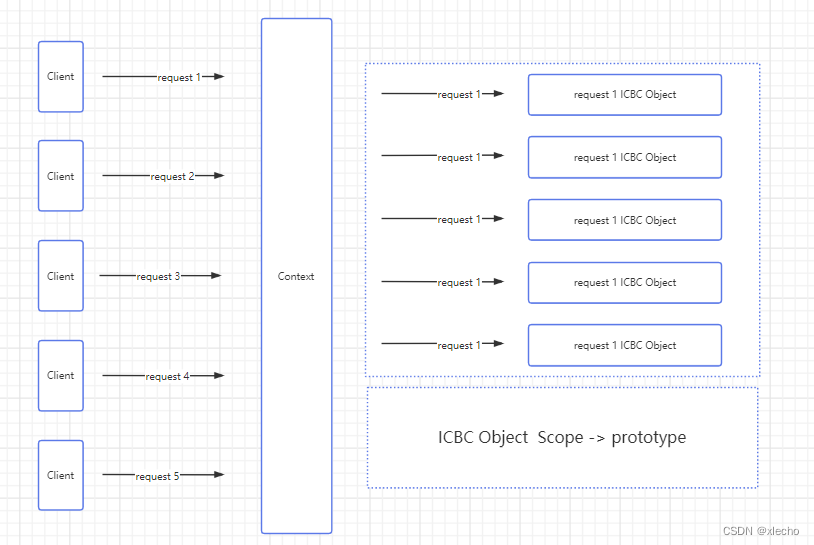
核心代码如下:
@Scope(value = "prototype")
@Component(value = "102")
public class ICBC10201 extends AbstractProcessHandler {
……
}
ProcessHandler bean = SpringContextUtils.getBean(queryContext.getBankCode(), ProcessHandler.class);
每一次请求都使用一个独立的对象,对象内无公共变量,保障整个请求链上没有对其他的请求暴露出来的数据,真正有效的规避数据安全风险。
解决高并发痛点,同时优化设计为对接多个银行提供统一标准。也许还有更多的优秀方案能够完美解决这些痛点,当前项目也不一定完美,对于技术的使用可能也会有些不尽人意。这里并不完美,希望更多的大佬们斧正。
此处可能存在不合适展示的内容,页面不予展示。您可通过相关编辑功能自查并修改。
如您确认内容无涉及 不当用语 / 纯广告导流 / 暴力 / 低俗色情 / 侵权 / 盗版 / 虚假 / 无价值内容或违法国家有关法律法规的内容,可点击提交进行申诉,我们将尽快为您处理。